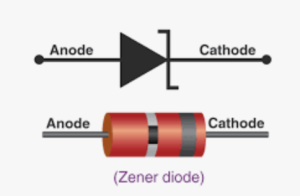
Zener diodes are essential components in electronics, known for their ability to regulate voltage by maintaining a stable output under reverse bias conditions. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to testing and distinguishing Zener diodes from regular diodes, ensuring their proper functionality in circuits.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Understanding Zener Diodes
- Function: Zener diodes operate in reverse bias, conducting current when the applied voltage exceeds the Zener voltage (Vz). This makes them ideal for voltage regulation, surge protection, and reference voltage applications.
- Key Difference from Regular Diodes: Unlike regular diodes, which block current in reverse bias until breakdown (often destructive), Zener diodes are designed to handle controlled reverse conduction at Vz.
2. Tools Required
- Digital Multimeter (DMM): For forward voltage and continuity tests.
- Variable DC Power Supply : To apply adjustable reverse voltage.
- Resistors: For current limiting (e.g., 1kΩ, 10kΩ).
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires: For circuit assembly.
- Datasheet (if available): For reference to Vz and power ratings.
3. Testing Methods
Method 1: Using a Multimeter (Diode Mode)
- Forward Bias Test:
- Set the multimeter to diode mode.
- Connect the red probe to the anode and black probe to the cathode.
- A healthy Zener diode will show a forward voltage drop of 0.6–0.7V, similar to a regular diode.
- Reverse Bias Test:
- Reverse the probes (black to anode, red to cathode).
- A regular diode will display “OL” (open loop). A Zener diode may also show “OL” if the multimeter’s test voltage (typically <3V) is below Vz.
Limitation: Most multimeters cannot supply enough voltage to trigger Zener breakdown. Use this method only for preliminary checks.
Method 2: Using a Power Supply and Resistor
Circuit Setup:
- Connect the Zener diode in reverse bias (cathode to positive supply).
- Place a current-limiting resistor in series (calculate using R=Vsupply−VzIR=IVsupply−Vz, where II is 5–10mA).
- Gradually increase the supply voltage while monitoring the voltage across the Zener with the multimeter.
Interpretation:
- Once the supply voltage exceeds Vz, the Zener will conduct, and the voltage across it will stabilize at Vz. For example, a 5V Zener will clamp the voltage to ~5V even if the supply reaches 12V.
Method 3: Curve Tracer or Component Tester (Advanced)
- Automated Testers: Devices like the Peak Atlas DCA Pro can identify Vz and generate characteristic curves.
- Oscilloscope with Function Generator: Plot the I-V curve to observe the breakdown voltage.
4. Distinguishing Zener Diodes from Regular Diodes
- Forward Bias: Both diodes behave similarly (~0.6–0.7V).
- Reverse Bias:
- Regular Diode: Shows “OL” until breakdown (often destructive).
- Zener Diode: Conducts at Vz without damage. Use the power supply method to confirm.
5. Determining Unknown Zener Voltage
- Step-Up Voltage Test:
- Start with a low voltage (e.g., 5V) and incrementally increase the supply while monitoring the Zener’s voltage.
- The point where the voltage stabilizes is Vz.
- Resistor Calculation Example:
- For a 12V supply and suspected 5V Zener: R=12V−5V0.005A=1.4kΩR=0.005A12V−5V=1.4kΩ (use 1.5kΩ).
6. Safety Tips
- Current Limiting: Always use a resistor to avoid exceeding the Zener’s power rating (P=Vz×IP=Vz×I).
- Heat Management: Ensure the diode doesn’t overheat during testing.
- Voltage Limits: Start with low voltages and incrementally adjust.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- No Voltage Regulation: The Zener may be shorted (replace) or open (no conduction).
- Incorrect Vz: Check for counterfeit components or incorrect markings.
- Overheating: Reduce test current or verify resistor value.
8. Conclusion
Testing Zener diodes requires understanding their unique reverse-bias behavior. While multimeters offer quick checks, a variable power supply and resistor provide reliable Vz measurement. Distinguishing them from regular diodes hinges on observing controlled reverse breakdown. Always prioritize safety by limiting current and voltage during tests.
By following this guide, you can confidently verify Zener diode functionality and integrate them effectively into your projects.
- Everything You Need To Know About Limit Switch - May 21, 2025
- Everthing You Should Know About Rheostat - May 20, 2025
- Everything You Need To Know About Reversing Contactor - May 19, 2025